Knowing the right user research questions to ask is vital to the success of your UX research. Research is an invaluable source of input for product development, but before you can get started, you need to make sure the questions lined up will get the insights you need, without influencing the data.
Think of this article as your guide to all-things user research questions: what to ask, how to ask it, and how to create your own questions. Let’s get started.
What kind of user research questions are there?
The kind of questions you ask will depend on your research goals—are you looking to gather user feedback, or find out if a particular feature is (or would be) useful? Are you trying to discover what problems bother your user, or whether they’d prefer one solution over another?
Before planning your questions and diving head-first into research, look at your overarching research plan and objectives. Consider this on a project-by-project basis, as your end questions will be drastically different depending on where you are in the product development process. For instance, if you’re in early product discovery, you may want to discover user intent and pain points. Or, if you’re working on a high-fidelity prototype, you might want to see how users interact with the prototype, and how easy it is to use. Asking questions at different stages of your process is a big part of continuous product discovery and ensuring your product remains the best it can be.
💡 If you’re looking to understand the types of question format used in surveys or user questionnaires, take a look at our guide on how to write survey questions.
User research questions can be categorized in many ways—by objective, research scenario, or point in the product journey, to name a few. Since different questions may apply in multiple situations, we’re going to consider questions organized by their research focus.
Questions for user research can typically be categorized three ways:
- Questions about the problem e.g., what are users’ pain points, what task are they trying to complete, what solution do they want
- Questions about the people e.g., who they are, how they use products, what they want to accomplish, how likely are they to use the product
- Questions about the product e.g., how users’ feel about content or design, can they navigate the product, how usable is it, what features do they like or dislike
Now we know what kinds of questions there are, let’s delve into the value of pre-made questions, and some examples of each question type.
Using pre-made user research questions
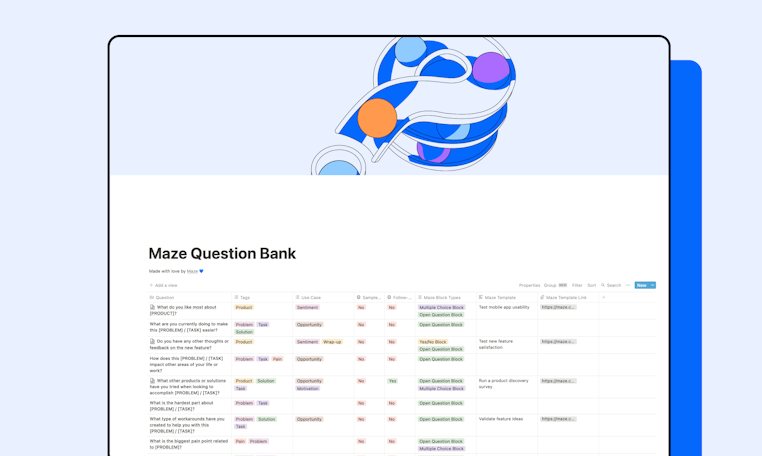
To elevate your research, you can opt to use pre-existing questions from a question bank. As with all research tools, there are many benefits to this, including saving time and effort, and having many questions to choose from. Using a question bank also ensures questions are always carefully considered, easily understandable for users, and unbiased.
A good question bank will be multifunctional, with questions you can use when running moderated to unmoderated testing, conducting generative or evaluative research, or gathering quantitative or qualitative data. So you can have one place to go for all your user research question needs.
🚀 Boost your research with Maze templates
If you’re a Maze user, you can also use the question bank as a handy companion to fuel your team’s research with Maze—check out the templates column and question block suggestions for maximum efficiency when building mazes.
Ultimately, a pre-made question bank can help save you a lot of time, and allow you to focus on conducting the research and processing analysis.
If you’d like to create your own questions, let’s get into the different user research question types, what questions they include, and how to ask them.
Questions about the problem
To support product and design decisions behind any solution, you need to be familiar with the problem you (and your users) are trying to solve. Whether you’re starting product discovery and want to understand user pain points, or you’re testing new features and want to gauge which will be most popular—you can’t begin working on a solution until you’ve honed in on what the problem is.
What’s bothering your users? How can you make their lives easier? What’s their key challenge, and what are they trying to achieve that’s being blocked by that problem?
Only once you’ve narrowed down a key problem statement can you translate solutions into the user experience, and identify opportunities for product development.
Questions focusing on the problem you’re trying to solve are key in product discovery stages and concept validation. The reason for using a particular product or feature may vary between users—consider Instagram’s Explore tab: it could be used to find friends, connect with like-minded people, or find inspiration.
Questions that can help hone into the problem at hand include:
- What problems do you face when you do [task]?
- Please complete this sentence: "The most frustrating part of trying to complete [task] is…”
- What is your main goal when trying to complete [task]?
- What is your personal measure of success when it comes to [goal]?
- How are you currently solving [problem]?
- Describe your ideal solution to [problem]
Questions about the people
Understanding the problem you’re trying to solve goes hand in hand with the people who are facing this problem—who they are and how they think, how they adopt and use products, their wants, needs and dislikes.
Put simply, there’s no point building a product if it solves the problem your user is having—but not in the way they wanted it to.
To really understand how your users think, and the way they approach a product, you need to understand their mental models. Broadly speaking, a mental model determines how someone forms their thinking process—it might impact the way they approach a problem, the kind of solution they’d like, and how they expect certain features to work.
UX research methods like card sorting are a good way to understand people’s mental models, but you can also gather this insight through thoughtful user interviews or research questions.
User-focused questions also cover understanding attitudes towards product adoption, use habits and circumstances, pricing models, and demographics.
Some example questions you could ask to learn more about your target users include:
- Are there any products that you prefer to use to do [task]?
- What does your job look like in your company?
- How do you prefer to be trained on new products?
- How much would you pay for [product]?
- Please describe who you might collaborate with when [task]?
- How often do you do [task]?
Questions about the product
Once you understand the problem your product will solve, and the people who’ll be using it, it’s time to circle back to the product itself. Questions about the product may be about its usability, what features you’re including, how users feel about content or design, and whether it does what they need it to.
Just like all research, it’s a good idea to ask product-related questions multiple time during the research phase, as both questions and answer will vary depending on what development stage you’re at—from prioritizing which feature to focus on developing first, to assessing how navigable a certain product section is, or reviewing the appeal of specific design aspects.
To gain a well-rounded understanding of how users find using your product or feature, usability testing is imperative. And, if you’re trying to nail down product navigation and identify any bumps in the user journey, tree testing is the research method of choice.
Whatever your focus, questions relating to the product are useful in both evaluative and generative research, and critical for creating a user-centered, solution-focused product.
Sample questions you can use to learn more about the product and features could include:
- How did you find the language (including but not limited to copy, phrasing, tone) used on the website?
- What’s the single most important thing we could do to make [product] better?
- On a scale of 1-10, how was your experience when [task]?
- Was the product navigation as expected?
- If you could change one thing about the design what would it be and why?
- Thinking about what [product] offers, which of the following best describes your feelings about it?
🤔 To dive into the questions you should be asking during usability testing, check out how to ask effective usability testing questions.
Regardless of what questions you ask, it’s worth bearing in mind that this information should be considered a guide, not a rule—as sometimes what people think they’ll do is not what they always do in practice. This is why it’s so important to continue research and testing in all stages of product development, so you can always be working off the most reliable and up-to-date insight.
Guidelines for crafting the right user research questions
Research questions set the standard of the data you’ll gather with them, so it’s crucial to properly craft each question to maximize insight and ensure accurate results.
Using a pre-made question bank is one way to keep questions effective, but if you’re writing your own questions, bear in mind that everything from the language you use to the structure or format of questions can influence the user’s answer.
The best questions for user interviews and research are clear, precise, and unbiased. Let’s go over some ultimate tips for crafting questions that fulfill this.
Stay neutral: avoid leading questions
One of the most important points when it comes to any research is being a neutral party, which means removing cognitive bias from your work. Research isn’t helpful if it’s biased, so ensure your questions are as impartial as possible—after all, just because you like Concept A over Concept B, doesn’t mean everyone will.
The key to staying neutral is avoiding leading questions where you subconsciously favor one thing over another, or plant an opinion or idea in the user’s mind, such as “How would you use concept A?”—this assumes they preferred concept A, which they may not have. Instead, try asking which concept they would use, followed by how they would use it.
Take it one question at a time
The majority of us think best when our minds are clear and able to focus on one thing, so avoid bombarding research participants with multiple questions phrased together.
Rather than asking a question like “What did you think about the design, copy and layout of the page?”, ask individually about the design, copy, and layout. Otherwise, you risk users merging their thoughts into one answer, when in fact they may feel very differently about each element.
Of course some questions lend themselves to being combined (e.g., “Which concept did you prefer and why?”), but it’s best to keep things separate when possible, and ask “Why?” in follow up questions, to allow users space to think and form individual answers for each question.
Ask open-ended questions
Similar to ensuring questions are unbiased, it’s also a good idea to ask open-ended questions—that is, to avoid questions which result in simply a ‘yes’ or ‘no’ answer.
The benefit of open-ended questions is that they give participants an opportunity to expand on their answer, work through their experience, and share details with you that may otherwise be missed. Consider that, while asking “Did you like the product?” may answer whether a user liked it, you’ll be left wondering what it is they like about it. Instead, try framing questions in a way that provides space for additional information, e.g. “What did you think about the product?”.
Pro tip ✨ If you do ask closed-ended questions, always keep follow up questions aside to dig deeper gather and extra insight from your participants.
Help users find their own voice
The language we use is incredibly powerful. Used well, words can move us, sway our opinions, educate us, and more.
By helping your research participants to find their own voice, you can unlock powerful statements and user insights which will truly impact your product. Formatting questions with the user at the center—using ‘you’ and asking emotive questions—builds empathy with the user and encourages them to find and share their own opinions through honest answers.
Ask questions you think you know the answer to
Our final question-crafting tip is to use research questions to test and validate your own assumptions and opinions. Ask questions you think you know the answer to—if you believe all users will prefer one new feature over the other, see if you’re right. If you think a certain design element works better on a different page, ask research participants to determine where they prefer it.
As with any research, while you may be user-adjacent, you are not your users. You are the expert in your product; they are the expert in using your product. Trust their opinions, and use their knowledge and experience to confirm your suspicions, or disprove them. Either way, you gain valuable insights.
User research is as effective as the questions you ask
Whether you’re investigating user preferences or conducting usability testing, research is only as effective as the questions you ask—and how you ask them.
Focus on questions that fit your research objectives, phrase your questions in the best way possible, and work to build empathy with your user; you’ll be able to gather valuable insights in no time.
Frequently asked questions and user research questions
What makes a good user research question?
What makes a good user research question?
A good research question is open-ended, unbiased, clear, and precise. It helps research participants share their thoughts, feedback, and opinions with researchers, without influencing or limiting their responses.
What type of user research questions are there?
What type of user research questions are there?
User research questions can broadly be broken down into three categories:
- Questions about the problem e.g., what are users’ pain points, what task are they trying to complete, what solution do they want
- Questions about the people e.g., who they are, how they use products, what they want to accomplish, how likely are they to use the product
- Questions about the product e.g., how users’ feel about content or design, can they navigate the product, how usable is it, what features do they like or dislike
How do you create a user research question?
How do you create a user research question?
There are several ways to create a user research question: you can either write your own question, or select premade questions from an existing research question bank.
If you choose to write your own research questions, it’s important to keep them clear and precise above all else—focus on asking questions that encourage users to open up, share additional information, and speak honestly.